What is electric current and the SI unit of current ampere
What is electric current?
Electric current can be defined as the measure of flow of sub-atomic charge carrying particles (in this case electrons) at any point of a conductor (wire) per unit time.
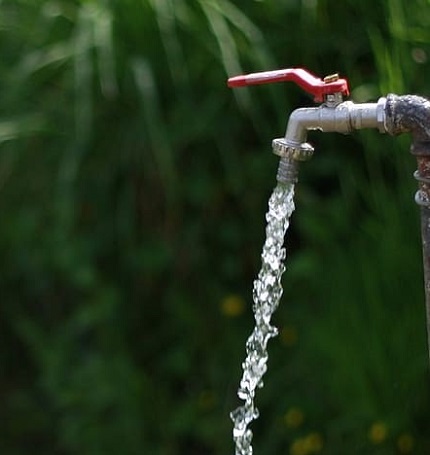
In electricity, the term current is used to express flow, similar to other currents in nature. As an example, consider water current. Refer below image of water flowing inside a pipe. Concept of electrical current is similar to water current that is flowing through a pipe.

Examples of sub-atomic particles having charge are electrons (negative charge) and protons (positive charge). Neutrons are neutral, without charge. Ions (atoms that have lost or gained electrons) are also charged, with positive or negative charge.
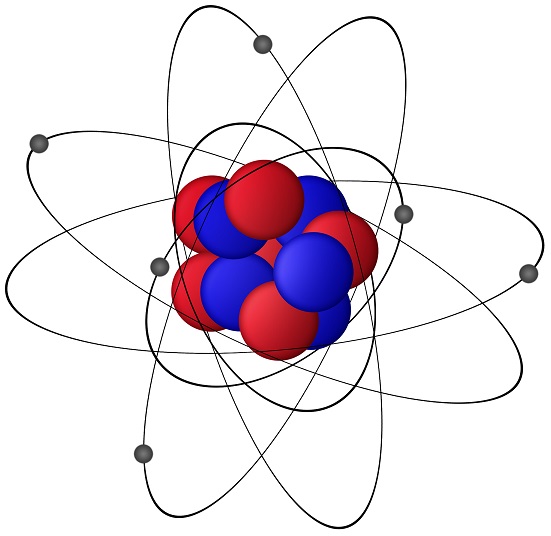
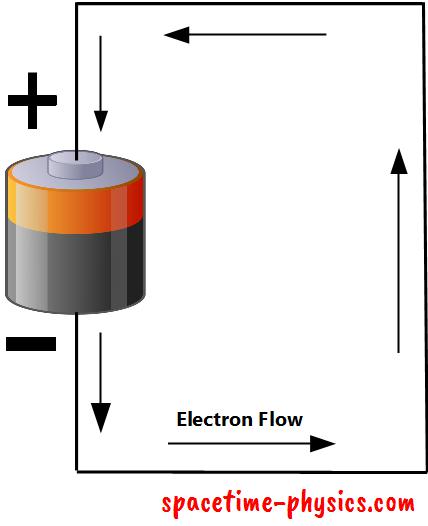
Particles with same charge repel (example: proton and proton) each other, and the particles with opposite charge (example: proton and electron) attract each other. As described above, electrons are negatively charged sub-atomic particles. Hence, electrons are attracted to the positive terminal of the battery. Electrons in an electrical circuit flow from the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal of the battery, through the conductor (wire) to form an electrical circuit. The flow of electrons in an electric circuit from negative terminal to positive terminal is called electron current flow.
What is the SI unit for electric current?
The SI units for electric current is "ampere". Unit of electric current, "ampere" is one of the seven base SI units. ampere is represented by symbol "A"
The SI unit of electric current "ampere" was named in honor of famous French physicist and mathematician Andre Marie Ampere.

SI unit of electric current ampere can be defined as 1 coulomb of charge passing through a point in an electric circuit in one second (SI unit for time, t). SI unit for charge (represented by Q) is coulomb.
Current = Charge / time (I = Q / t).
1 ampere = 1 coulomb per second.
Another important equation related with electric current is given below
The relationship between the voltage (V), resistance (R), and current (I) is defined in Ohm's law.
V=IR, where V is voltage and R is resistance.
Above equation can be rewritten as I = V/R. This equation says that the current is directly proportional to the voltage across two points of a conductor.